Facts and data on pictograms

Synonyms / Other Terms Used
ORL, E.N.T. Department, E.N.T. Ward, Ear, Nose, and Throat, Otorhinolaryngologist, Otolaryngologist, ENT Physician, ENT Surgeon
Category
Public Services, Public Facilities, Health Care, Clinical Facilities
Message / Function
To indicate the location of a clinical facility that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders especially regarding ear, nose, throat, and neck
| Source | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 |
Dreyfuss | Side view of head with ear in outline, oral cavity and throat indicated as sectional view |
 |
Cristian Lungu | Side view of head with ear, oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated as sectional view |
 |
CNIS | Side view of head with ear, nasal cavity, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated as sectional view |
 63 63 |
Hablamos Juntos | Side view of head with ear, oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated by lines |
 50 50 |
Hablamos Juntos | Side view of head with eye and ear, nasal cavity, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated by dotted lines |
 |
SEGD/HJ | Side view of head with eye and ear, oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated by dashed lines |
 70 70 |
Hablamos Juntos | Side view of head with eye and ear, oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated by dashed lines |
 |
D'source | Side view of head with eye and ear, oral and nasal cavities, and throat indicated as sectional view |
 |
NYCHHC | Side view of head with ear, throat, oral and nasal cavities indicated as sectional view |
 |
Erco | Side view of head in outline, lines indicating nose, oral cavity and ear |
 |
Aicher OAP | Side view of head in outline, lines and dots indicating nose, ear and throat |
 |
Aku-Johnson | Side view of head with ear, oral cavity and throat indicated by line |
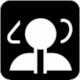 10 10 |
Hablamos Juntos | Front view of head, neck, and shoulders with throat indicated, between nose and ear in outline |
 13 13 |
Hablamos Juntos | Side view of medical instruments including otoscope |
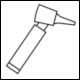 |
Saliuk | Side view of an otoscope or auriscope |
Note: Some of the examples shown above were mirrored horizontally to contrast differences.
Discussion
The examples shown above indicate that there might be a visual stereotype to indicate a clinical facility that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders especially regarding ear, nose, throat, and neck: A side view of a head displaying an ear and including some kind of rendering of oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube. Other pictograms are rare and mostly focus on medical instruments used in Otorhinolaryngology.
We found only two studies that present research covering pictogram variants for this referent:
Hablamos Juntos in partnership with SEGD (the Society for Environmental Graphic Design) developed several test designs to signify Health Services, services to improve general physical and mental well being, of which five pictograms were subjected to a test on basis of the Comprehensibility Estimation procedure (Fontaine et al., 2010). With median scores ranging from 70 down to 10 none of the pictograms examined was judged as well comprehensible. The numbers next to the pictograms in the table above are the median estimation scores reported for the corresponding pictograms in this study. Regarding these results a new variant - labeled as SEGD/HJ above - was designed on basis of the variant rated as most comprehensible.
In a follow up project this symbol was examined - among others - by Zender & Cassedy (2014) using the ISO/ANSI Open-ended Comprehension Test to find out if this variant is understood just as well in a different culture, and if not, why it does not work. Test results from the United States and Tanzania reveal that the side view of a head with eye and ear, oral and nasal cavities, throat, and pharyngotympanic tube indicated by dashed lines, labeled SEGD/HJ in the table above, basically might work to a certain extent in the USA, as 74 % of the responses from the American sample could be classified as correct. But in the Tanzanian sample it became evident that this variant does not work everywhere: it neither performed well among respondents with advanced medical literacy, nor among typical local patients with 18 % correct for the whole sample. The failure was considered to be due to insufficient knowledge about this medical specialization.
In our database we did not find comprehensibility data concerning some other image contents shown, as for example the side view of an otoscope or auriscope.
Recommendations
Due to the fact that data from research is insufficient, we recommend testing using the Comprehensibility Estimation procedure for eliminating poor variants and identifying the best of the set available, followed by a Comprehension Test. These studies should deliver useful data for recommending the best pictogram. Detailed information about the most frequent responses given in each of the response categories of the Comprehension Test should be provided to correctly judge comprehensibility and improve designs. Also information concerning knowledge about this medical specialization should be collected at the end of the test, as studies suggest that many terms used for healthcare facilities are often not understood well by people visiting hospitals or related institutions.
Tests of pictograms of referent Otorhinolaryngology
Fontaine, L., Fernández, O., & Middleton, D. (2010): Universal Symbols in Health Care - Symbol Design Research Report. SEGD.
Zender, M., & Cassedy, A.E. (2014): (Mis)understanding: Icon Comprehension in Different Cultural Contexts. Visible Language, 48, 69.
See also
Hospital, Doctor, Health Care Center
Updated 2024-10-05 by Ch.Brugger